英语翻译GROWTH OF BACTERIOPHAGES IN THE LABORATORYThe plaque met
来源:学生作业帮 编辑:大师作文网作业帮 分类:英语作业 时间:2024/11/18 06:54:24
英语翻译
GROWTH OF BACTERIOPHAGES IN THE LABORATORY
The plaque method:
1.Mixes bacteriophages with host bacteria and nutrient agar.
2.After several viral multiplication cycles,the bacteria in the area surrounding the original virus are destroyed; the area of lysis is called a plaque.
3.Each plaque can originate with a single viral particle or with more than one; the concentration of viruses is given as plaque-forming units.
GROWTH OF ANIMAL VIRUSES IN THE LABORATORY
1.Cultivation of some animal viruses requires whole animals.
2.Some animal viruses can be cultivated in embryonated eggs.
3.Cell cultures are cells growing in culture media in the laboratory.
4.Viral growth can cause cytopathic effects in the cell culture.
VIRAL IDENTIFICATION
1.Serological tests are used most often to identify viruses.
Viruses may be identified by restriction enzyme fragments and
nucleic acid base sequencing.
2.Viral Multiplication
1.Viruses do not contain enzymes for energy production or protein synthesis.
2.For a virus to multiply,it must invade a host cell and direct the host's metabolic machinery to produce viral enzymes and components.
GROWTH OF BACTERIOPHAGES IN THE LABORATORY
The plaque method:
1.Mixes bacteriophages with host bacteria and nutrient agar.
2.After several viral multiplication cycles,the bacteria in the area surrounding the original virus are destroyed; the area of lysis is called a plaque.
3.Each plaque can originate with a single viral particle or with more than one; the concentration of viruses is given as plaque-forming units.
GROWTH OF ANIMAL VIRUSES IN THE LABORATORY
1.Cultivation of some animal viruses requires whole animals.
2.Some animal viruses can be cultivated in embryonated eggs.
3.Cell cultures are cells growing in culture media in the laboratory.
4.Viral growth can cause cytopathic effects in the cell culture.
VIRAL IDENTIFICATION
1.Serological tests are used most often to identify viruses.
Viruses may be identified by restriction enzyme fragments and
nucleic acid base sequencing.
2.Viral Multiplication
1.Viruses do not contain enzymes for energy production or protein synthesis.
2.For a virus to multiply,it must invade a host cell and direct the host's metabolic machinery to produce viral enzymes and components.
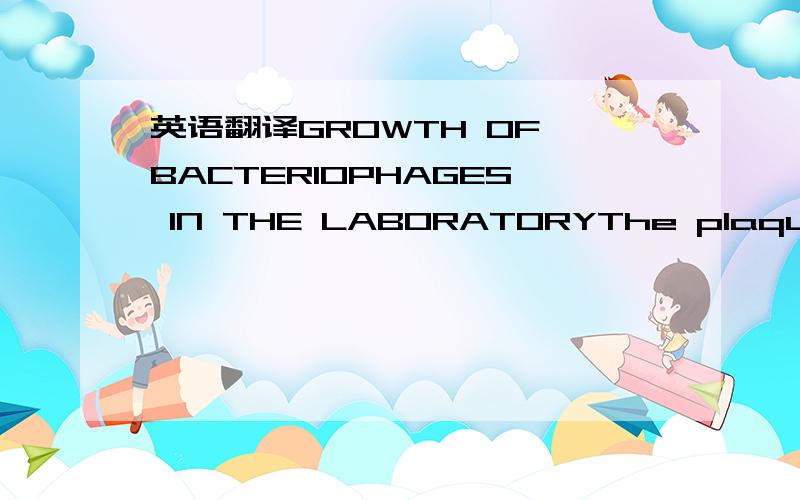
一. 液体培养法
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将噬菌体原液100 μl 与寄主细菌悬浮液300 μl均匀混合,静置15分钟使其感染.
3. 将混合液接种至含10 ml新鲜液体培养基的试管中,于适当温度下振荡培养约8~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
4. 将培养液移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟,以沉淀寄主细菌.
5. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.但因噬菌体原液呈透明状,无法以肉眼直接判断其增殖效果,故应测定其效价以确认增殖培养之成效.
二. 双层琼脂培养法
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将噬菌体原液100 μl 与寄主细菌悬浮液300 μl均匀混合,静置15分钟使其感染.
3. 将混合液加入5 ml 冷却至45℃的0.7%琼脂培养基中,均匀混合后立即平铺在已倒好的1.8%琼脂培养基平板上.
4. 待平板凝固后移至适当温度之培养箱中,一般培养8~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
5. 以上述相同之步骤制作另一不含噬菌体之对照组.
6. 将培养好的平板与对照组比较其澄清度,一般含噬菌体之平板呈澄清状,而仅含寄主细菌之对照组则呈混浊状.
7. 将含有噬菌体之平板置于 -20℃下4~5小时后,取出置于室温下解冻.
8. 将解冻后产生的液体移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟以沉淀寄主细菌.
9. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22 μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.
三. 表面琼脂培养法
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将寄主细菌悬浮液3 ml均匀平铺于1.8%琼脂培养基平板上,静置2小时.
3. 将多余的寄主细菌悬浮液吸出,再将噬菌体原液0.3 ml均匀涂抹于平板上.
4. 于适当温度下培养约16~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
5. 取5 ml 新鲜液体培养基加入平板中,以 L 形玻棒刮洗下平板表面之菌体.
6. 将刮洗下之液体移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟以沉淀寄主细菌.
7. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22 μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将噬菌体原液100 μl 与寄主细菌悬浮液300 μl均匀混合,静置15分钟使其感染.
3. 将混合液接种至含10 ml新鲜液体培养基的试管中,于适当温度下振荡培养约8~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
4. 将培养液移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟,以沉淀寄主细菌.
5. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.但因噬菌体原液呈透明状,无法以肉眼直接判断其增殖效果,故应测定其效价以确认增殖培养之成效.
二. 双层琼脂培养法
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将噬菌体原液100 μl 与寄主细菌悬浮液300 μl均匀混合,静置15分钟使其感染.
3. 将混合液加入5 ml 冷却至45℃的0.7%琼脂培养基中,均匀混合后立即平铺在已倒好的1.8%琼脂培养基平板上.
4. 待平板凝固后移至适当温度之培养箱中,一般培养8~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
5. 以上述相同之步骤制作另一不含噬菌体之对照组.
6. 将培养好的平板与对照组比较其澄清度,一般含噬菌体之平板呈澄清状,而仅含寄主细菌之对照组则呈混浊状.
7. 将含有噬菌体之平板置于 -20℃下4~5小时后,取出置于室温下解冻.
8. 将解冻后产生的液体移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟以沉淀寄主细菌.
9. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22 μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.
三. 表面琼脂培养法
1. 将指定之寄主细菌以液体培养法于适当温度下培养,一般培养16~24小时.
2. 将寄主细菌悬浮液3 ml均匀平铺于1.8%琼脂培养基平板上,静置2小时.
3. 将多余的寄主细菌悬浮液吸出,再将噬菌体原液0.3 ml均匀涂抹于平板上.
4. 于适当温度下培养约16~24小时,培养时间依噬菌体之不同而异.
5. 取5 ml 新鲜液体培养基加入平板中,以 L 形玻棒刮洗下平板表面之菌体.
6. 将刮洗下之液体移入离心管中,以10,000 rpm (5,000 g)离心10分钟以沉淀寄主细菌.
7. 将上清液移至新管中,以0.22 μm孔径之过滤器(filter)去除残余菌体,即得不含寄主细菌之噬菌体原液.
英语翻译Ditch The CalculatorThe growth in the use of calculators
英语翻译The growth of limited liability companies resulted in __
英语翻译The growth in the number of people of marriageable age t
英语翻译in this process of recrystallization,the growth of new c
英语翻译In spite of these issues,the rare of online growth does
英语翻译In a forest of mixed growth somewhere on the eastern spu
英语翻译the growth rate of output is equal to the growth rate of
英语翻译Hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) is the hallmark of
英语翻译One misconception about the growth of the service sector
英语翻译The growth of the Limited Liability Company and municipa
英语翻译The remarkable period of rapid economic growth that has
英语翻译Hence higher population growth can increase the rate of